Navigating the Mediterranean Diet: A Journey to Wellness
The Mediterranean diet has long been celebrated as one of the healthiest eating patterns in the world. Rooted in the traditional culinary practices of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this diet has captured the attention of nutritionists, researchers, and health-conscious individuals alike. Its emphasis on plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of lean proteins has been linked to numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, certain cancers, and cognitive decline. The Mediterranean diet is not just a set of dietary guidelines; it's a lifestyle that encompasses social connections, physical activity, and a mindful approach to eating. As more people seek sustainable ways to improve their health, the Mediterranean diet continues to gain traction as a balanced and enjoyable approach to nutrition.

Cultural aspects, such as communal meals and the enjoyment of food, are integral to the Mediterranean lifestyle. Meals are often social events, shared with family and friends, fostering a sense of connection and well-being. This emphasis on community and pleasure in eating contributes to the diet’s sustainability and appeal.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
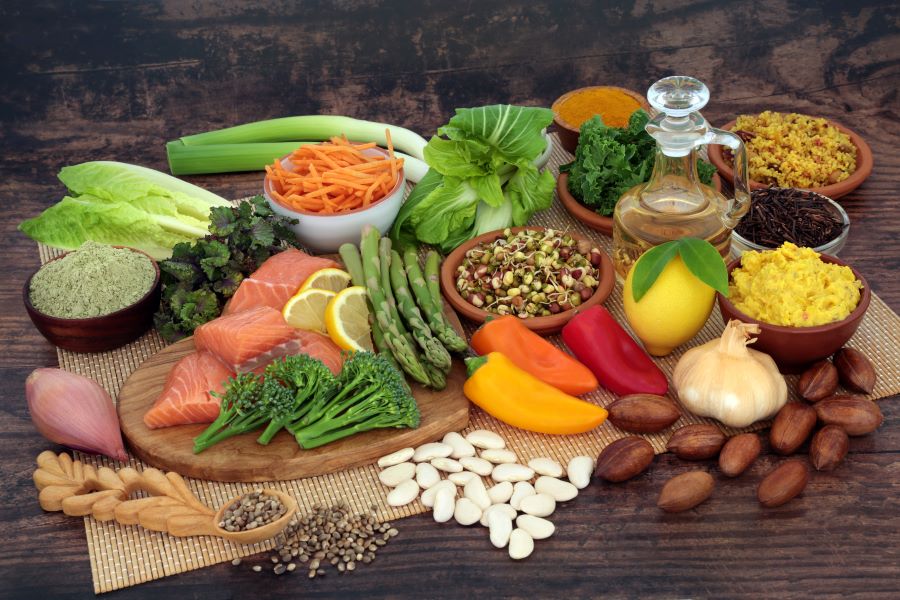
At the heart of the Mediterranean diet is a focus on plant-based foods. Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds form the foundation of most meals. These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health. Olive oil, a staple in Mediterranean cuisine, serves as the primary source of fat, offering monounsaturated fats and polyphenols with anti-inflammatory properties.
Fish and seafood are consumed regularly, providing omega-3 fatty acids and lean protein. Poultry, eggs, and dairy are included in moderate amounts, while red meat is limited to occasional consumption. Herbs and spices are used generously to add flavor without relying on excessive salt. Additionally, moderate consumption of red wine with meals is common in many Mediterranean cultures, though it’s not a requirement for following the diet.
Health Benefits and Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have demonstrated the positive health impacts of the Mediterranean diet. A landmark study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2013 showed that adherence to this dietary pattern significantly reduced the risk of major cardiovascular events. The diet has also been associated with lower rates of type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
The Mediterranean diet’s health benefits are attributed to its combination of nutrients and compounds. The high intake of fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish and monounsaturated fats from olive oil contribute to heart health and improved cholesterol profiles. The diet’s emphasis on whole grains and legumes helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and promotes digestive health.
Adapting the Mediterranean Diet in Modern Times
While the traditional Mediterranean diet evolved in a specific geographical and cultural context, its principles can be adapted to various lifestyles and cuisines worldwide. The key is to focus on the overall pattern of eating rather than specific ingredients. For example, individuals in non-Mediterranean regions can incorporate local seasonal produce and whole grains while maintaining the diet’s emphasis on plant-based foods and healthy fats.
Modern interpretations of the Mediterranean diet often include considerations for sustainability and environmental impact. This may involve choosing locally sourced, organic produce when possible and reducing meat consumption to align with both health and environmental goals. Additionally, the rise of plant-based alternatives has made it easier for those following vegetarian or vegan diets to adhere to Mediterranean principles.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, adopting the Mediterranean diet can present challenges for some individuals. The diet’s reliance on fresh, whole foods may require more time for meal preparation and planning. Additionally, the cost of certain ingredients, such as high-quality olive oil and fresh fish, can be a barrier for some.
Cultural differences and food preferences can also impact adherence to the diet. For those accustomed to diets high in processed foods or red meat, the transition to a more plant-based eating pattern may require gradual changes and experimentation with new recipes and flavors.
It’s important to note that while the Mediterranean diet is generally considered safe and beneficial for most people, individual nutritional needs may vary. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help ensure that the diet is appropriately tailored to one’s specific health goals and requirements.
The Future of the Mediterranean Diet
As research continues to support the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet, its influence on global nutrition guidelines and public health policies is likely to grow. The diet’s flexibility and focus on whole foods make it a promising model for addressing various health concerns, from obesity to chronic disease prevention.
Emerging areas of study include the diet’s potential impact on gut microbiome health and its role in promoting longevity. Additionally, researchers are exploring how principles of the Mediterranean diet can be combined with other evidence-based dietary approaches to create personalized nutrition plans.
The Mediterranean diet represents more than just a set of dietary guidelines; it embodies a holistic approach to health that encompasses food, lifestyle, and cultural values. As the world grapples with rising rates of chronic diseases and the need for sustainable eating patterns, the Mediterranean diet offers a time-tested, enjoyable, and health-promoting approach to nutrition that continues to inspire and guide individuals toward improved well-being.